![]()
Test early, collaborate easily, deploy often
Today’s most sophisticated, engaging apps are built and deployed using modern development practices. These include optimized processes and workflows that increase developer productivity, efficiency, and speed, as well as improve app quality. Adoption of agile development practices and distributed version control systems have now become widespread. To complement these, a new practice has emerged—continuous delivery (CD)—that enables teams to streamline the app release process.
Continuous delivery features short release cycles, automation, and a direct connection to the source code repository. It's designed to enable teams to get incremental app updates to production quickly and safely. A successful CD process aligns an organization’s technology, processes, people, and culture so that deployment becomes a streamlined, automated activity. Businesses and end users benefit from faster delivery of new features and increased app quality.
Heroku Flow
The Heroku platform is designed to maximize developer productivity and provide a great developer experience, from an app’s first build to production and beyond. As part of this focus, Heroku extends the platform with a range of tools that support modern development practices, such as continuous delivery.
Heroku Flow is a structured deployment workflow that combines tight integrations with GitHub, visually presented pipelines, disposable “review apps” and Heroku CI. Heroku Flow is designed to streamline the app release experience by making continuous delivery easy, visual, and efficient.
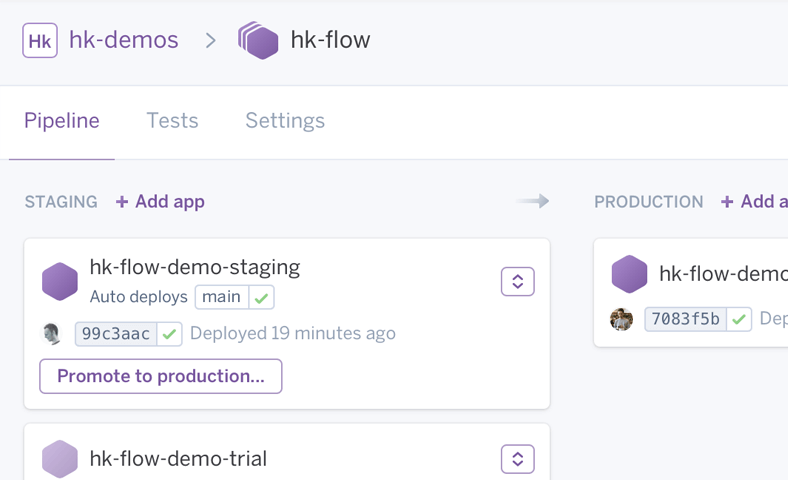
Heroku Pipelines
Heroku apps that share the same codebase can be organized into deployment pipelines, easily promoted from one stage to the next, and managed through a visual interface. Heroku Pipelines docs →
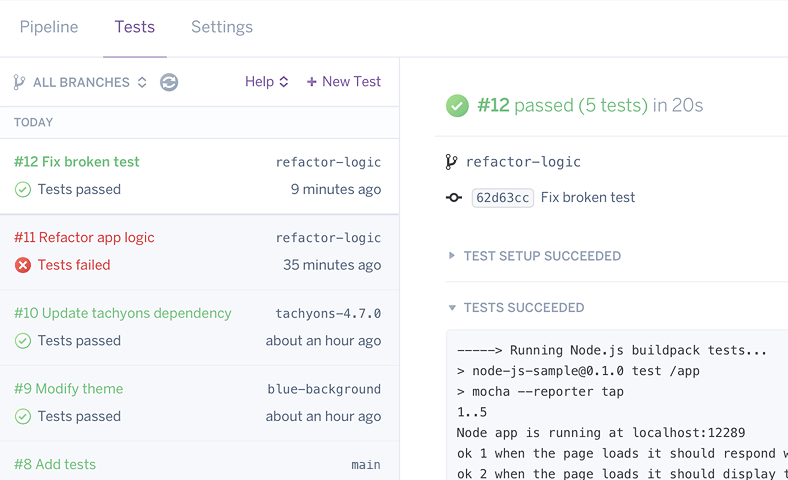
Heroku CI
Heroku CI is a low-setup, visual test runner that integrates with Heroku Pipelines to automatically run your tests on every push to GitHub, using disposable apps with strong dev-prod parity. Heroku CI docs →
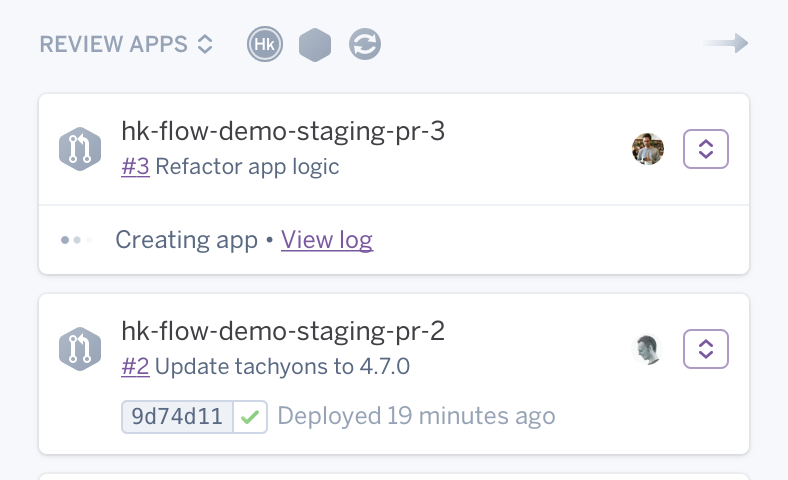
Heroku Review Apps
Developers can spin up a temporary test app for teams to review, discuss, and decide whether to merge changes to their code base during development. Heroku Review Apps docs →
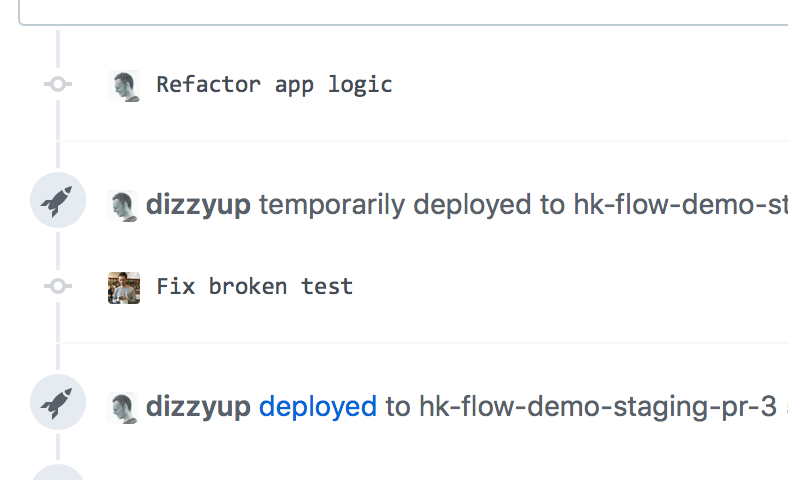
GitHub Integration
Tight integration between a Heroku app and its GitHub repo enables automatic or manual deployment of merged branches, with notifications in both GitHub and Heroku. GitHub Integration docs →
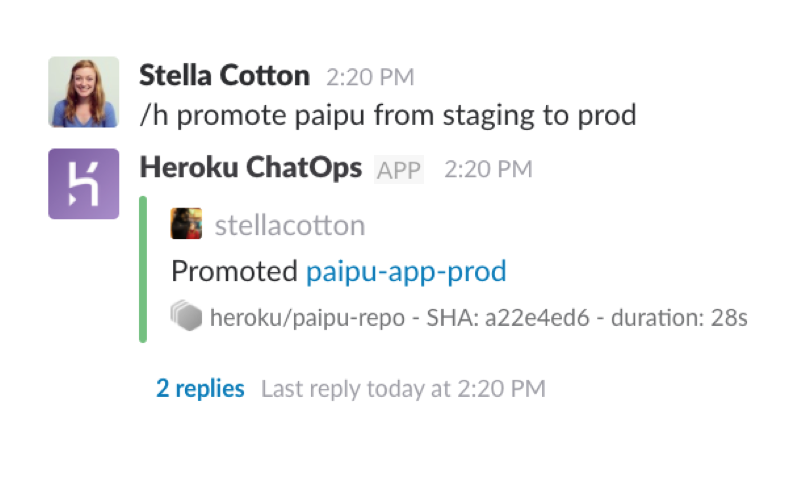
Heroku ChatOps
Heroku ChatOps makes team collaboration easier by connecting Heroku Pipelines with Slack. With Heroku ChatOps developers can deploy to staging or promote to production from Slack, or see pull requests, merges, and CI build results within their Slack channel. Heroku ChatOps docs →
Release Phase
Release Phase lets you automatically run tasks, such as database migrations, before a release is deployed to production. Release Phase eliminates risky manual deployment steps. Release Phase docs →
How continuous delivery works
At the heart of continuous delivery lies a basic branch-and-merge workflow. Multiple developers each work on their own code branch, share changes for peer review, feedback and approval, and seamlessly merge their updated code into the main branch. The process is straightforward and efficient, easily keeping pace with the speed of the team.
Benefits of continuous delivery
With continuous delivery, app releases become more like a drumbeat than a big bang. The practice offers a steady stream of benefits to engineering organizations, end users, and business stakeholders—without the disruption of the traditional release process.
Foundations of continuous delivery
A successful continuous delivery practice is founded on three core components that will help teams produce the best results:
Configuration management
When practicing continuous delivery, it’s vital that development teams establish a process and agree upon a common set of tools that ensure consistency across app performance, function, and user experience. Configuration management enables version control of all the parts of the CD process, such as source code, databases, documentation, test and deployment scripts, and app configuration information. Developers can then reproduce an environment when needed, and trace all dependencies used to re-create the environment. Having one source of truth—and a reliable one—provides a stable foundation on which to build a smooth deployment pipeline.
Continuous integration
In complex apps, changes that may seem simple and self-contained can actually produce unintended consequences. Multiple developers may be working in parallel on multiple code branches in isolated environments. When changes are merged to a common main branch, unpredictable results can occur. This often means multiple rounds of regression testing and bug fixes. Continuous integration (CI) is a component of the continuous delivery process that enables developers to integrate their updates into main on a regular basis. With CI, automated tests before and after the merge validate that no bugs have been introduced.
Automated testing
Traditionally, testing has been done manually after code is “dev complete” to ensure that any changes don’t break the app or its systems. However, manual regression testing is time-consuming, costly, and prone to human error. Moreover, QA teams have to spend considerable time and effort keeping test documentation up to date. With continuous delivery, many different tests are run throughout the process. Some are automated, such as unit tests. Others, such as usability/acceptance testing, are still performed manually. The goal is to bring all testing into the CD process from the beginning of the delivery lifecycle, and automate repetitive tasks as much as possible. This allows developers to focus on coding and improving the app.
Continuous delivery success factors
For a continuous delivery practice to thrive, everyone involved in an app’s development must share the mindset and habits that contribute to a smooth process. Every member of the team—from product managers to designers to developers—is responsible for the success of their part all the way to production. A few CD best practices will help orient the team right from the beginning.