Heroku Flow brings together Heroku Pipelines, Review Apps, Heroku CI and GitHub integrations into an easy-to-use structured workflow for continuous delivery.
App-centric continuous delivery, optimized for developers
New to continuous delivery, or have unanswered questions?
Heroku Flow brings together six key capabilities for continuous delivery
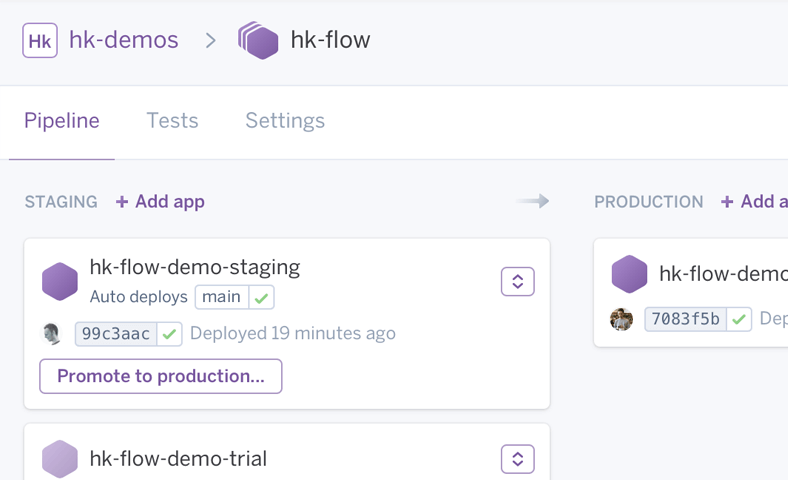
Heroku Pipelines
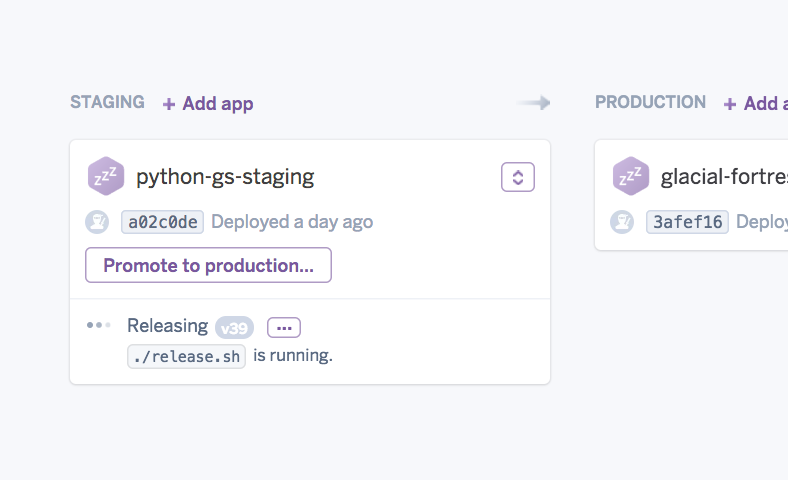
Pipelines is a way to organize a group of Heroku apps sharing the same codebase into review, development, staging, and production environments to support, manage and visualize continuous delivery. Promoting tested code from one stage to the next can be done manually or automatically and is nearly instantaneous, since the compiled artifact is promoted to the next stage. The Pipelines overview page in the Heroku Dashboard tracks the real-time progress of code and features from development to production. Heroku Pipelines docs →
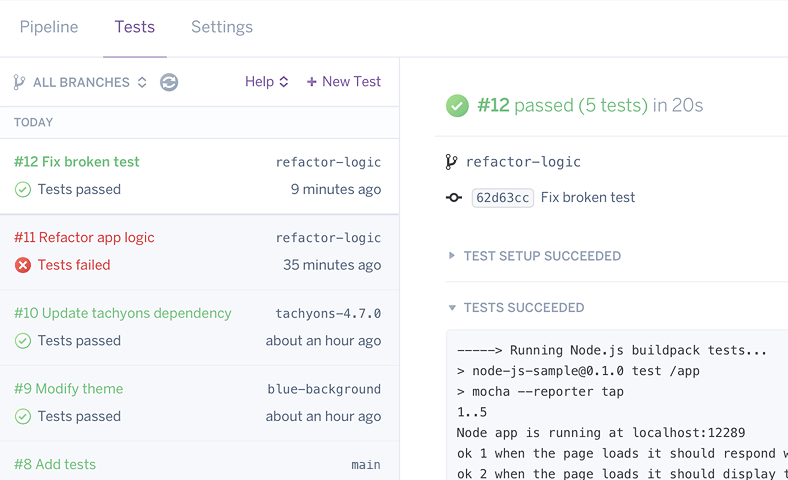
Heroku CI
Heroku CI is a low-configuration test runner that integrates with Heroku Pipelines. Heroku CI runs your test scripts with zero queue time for faster results, using disposable apps that have strong parity with your staging and production environments. Access test results from Heroku or GitHub, automate deployments conditionally on CI results, and take advantage of a fully visual interface built to support CI’s role in team-based continuous delivery. Heroku CI docs →
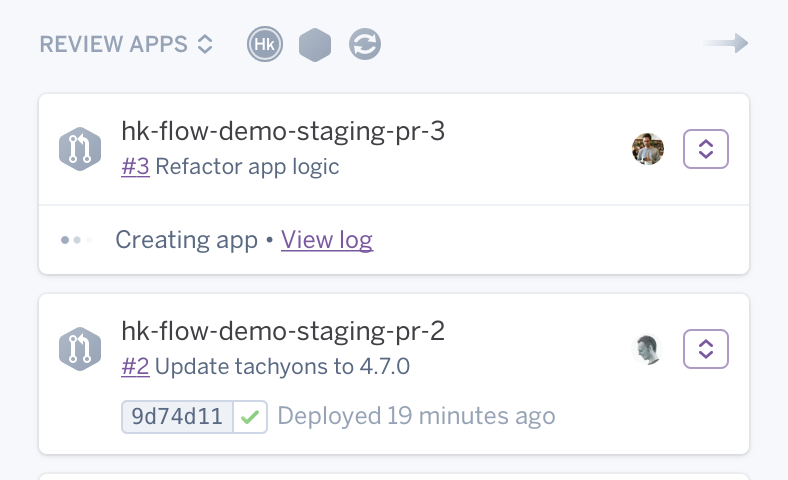
Heroku Review Apps
Review Apps are used to propose, discuss, and decide whether or not to merge changes to your code base. For Heroku apps connected to GitHub, you can manually spin up a temporary test app or automate it based on a unique URL for every opened pull request (PR). Merging the PR destroys the review app, and when used with Heroku Pipelines, automatically promotes the code to staging. Users can also leverage the Review App API, an extension of the Heroku Platform API, to more easily automate workflows or use Review Apps with different CI tools. Heroku Review Apps docs →
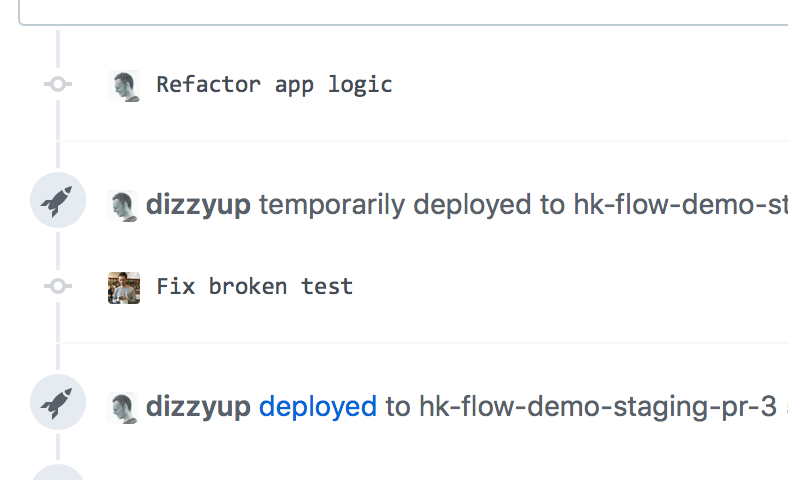
GitHub Integration
Connect your GitHub repo to a Heroku app to either manually or automatically deploy a particular branch on every GitHub push. For every deploy you can see the diff between the current release and the previous commit in the app’s Activity tab in the Heroku Dashboard, so you’re never guessing what code is on the app. If you’ve configured your GitHub repo to use an external continuous integration (CI) server, you can configure Heroku to only auto-deploy a branch after CI passes for a particular commit. GitHub Integration docs →
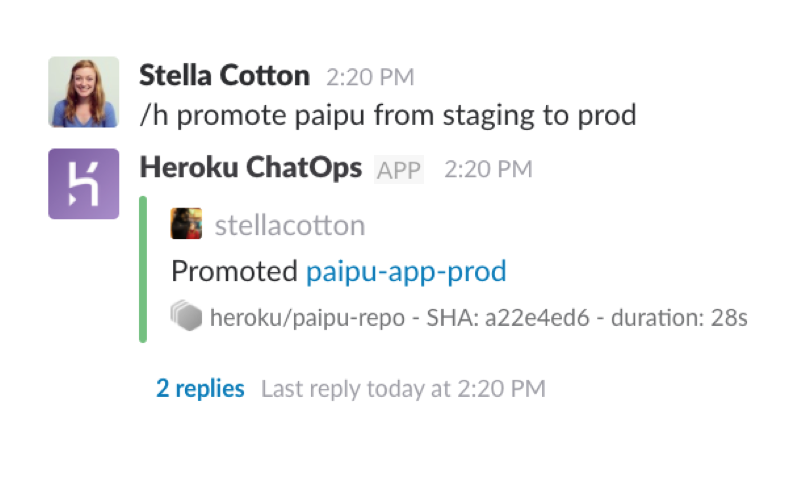
Heroku ChatOps
Heroku ChatOps uses the power of Heroku Pipelines to bring a collaborative deployment workflow to Slack. It enables developers to deploy to staging or promote to production from Slack. With Heroku ChatOps teams can keep track of all code changes within their Slack room. Pull request notifications, merges and CI build results all show up in Slack so no context switching is needed to see build results or check if promoting to production was successful. Heroku ChatOps docs →
Release Phase
Release Phase lets you run tasks before a release is deployed to production, eliminating maintenance windows, and reducing deployment risk. Migrate a database, upload assets to a CDN, invalidate a cache or run any other task your app needs to be ready for production. If a Release Phase task fails, the new release is not deployed, leaving the current production release unaffected. Release Phase docs →

